HashMap的存储结构
HashMap存储默认初始化一个16大小的Node数组,如果存在冲突,则在以链表的方式存储,如果链表长度达到临界值,则使用红黑树存储。如下:
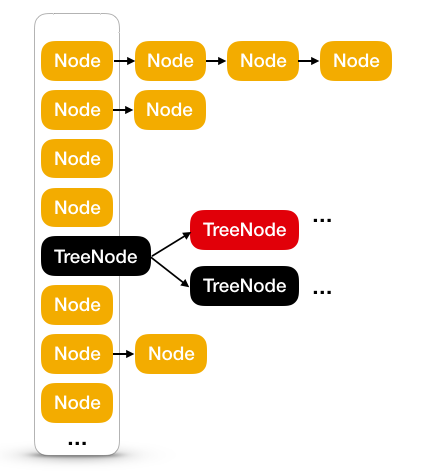
HashMap 扩容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// 如果为空则重新创建一个Node数组,数组即HashMap
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// 如果hash值对应的Node数组中的Node为空,则直接将key,value放入Node
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// 判断下key是否相同,如果相同获取此Node
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// 如果key不相同,判断下Node数组中的对应Node是否是树结构,树结构直接新增树节点
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
// 遍历Node数组对应位置Node的链表,将新增一个节点放入链表末尾。
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 如果增加后链表到达临界值,则转为树结构。
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// 如果链表中存在相同的key,则获取此节点,返回Node
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 如果存在key相同的Node,则获取旧值,
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
// 只有允许修改标识为true或者旧值为null时可以替换旧值
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
// 移动node至尾部
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 超过了阀值,重新扩展HashMap Node数组的大小
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
|
final Node<K,V>[] resize() {
Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table;
// 未扩展前 HashMap Node数组大小(容量)
int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;
// 旧阀值
int oldThr = threshold;
int newCap, newThr = 0;
// 如果未扩展前 HashMap Node数组大小大于0且大小大于等于最大容量值,则调整阀值到整数上线,然后返回旧Node数组,即HashMap,否则将旧阀值扩大一倍。
if (oldCap > 0) {
if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTab;
}
else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY)
newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold
}
// 旧容量为0,且旧阀值大于0,则将新容量设置为旧阀值
else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold
newCap = oldThr;
// 如果旧阀值且旧容量为0,则使用默认的容量大小和阀值因子
else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
// 新阀值如果为0,则使用新的容量和阀值因子计算。
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap];
table = newTab;
if (oldTab != null) {
// 遍历旧Node数组
for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) {
oldTab[j] = null;
if (e.next == null)
newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e;
else if (e instanceof TreeNode)
((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap);
else { // preserve order
Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null;
Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null;
Node<K,V> next;
do {
//遍历旧的链表
next = e.next;
// 这里的意思说,例如原来容量为16,现在扩展到32
// 容量为16时,使用15&hash获取key在Node数组中的位置,即1111&hash
// 容量为32时,使用31&hash获取key在Node数组中的位置,即11111&hash
// 看出来区别没有,如果hash值得第5位不为1,则位置不变,否则的话,位置为 16+原来的位置。
if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) {
if (loTail == null)
loHead = e;
else
loTail.next = e;
loTail = e;
}
else {
if (hiTail == null)
hiHead = e;
else
hiTail.next = e;
hiTail = e;
}
} while ((e = next) != null);
if (loTail != null) {
loTail.next = null;
newTab[j] = loHead;
}
if (hiTail != null) {
hiTail.next = null;
newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTab;
}
|
FAQ
- HashMap并发下死循环问题?
该问题在JDK1.8中已经修复了。不过还是不推荐并发情况下使用,容易造成数据丢失。
